कंप्यूटर
कंप्यूटर (अन्य नाम - संगणक, परिकलक; वस्तुतः एक
अभिकलक यंत्र (programmable machine) है जो दिये गये गणितीय तथा तार्किक
संक्रियाओं को क्रम से स्वचालित रूप से करने में सक्षम है। इसे अंक गणितीय,
तार्किक क्रियाओं व अन्य विभिन्न प्रकार की गणनाओं को सटीकता से पूर्ण
करने के लिए योजनाबद्ध तरीके से निर्देशित किया जा सकता है। चूंकि किसी भी
कार्य योजना को पूर्ण करने के लिए निर्देशो का क्रम बदला जा सकता है इसलिए
संगणक एक से ज्यादा तरह की कार्यवाही को अंजाम दे सकता है। इस निर्देशन को
ही कम्प्यूटर प्रोग्रामिंग कहते है और संगणक कम्प्यूटर प्रोग्रामिंग भाषा
की मदद से उपयोगकर्ता के निर्देशो को समझता है। यांत्रिक संगणक कई सदियों
से मौजूद थे किंतु आजकल अभिकलित्र से आशय मुख्यतः बीसवीं सदी के मध्य में
विकसित हुए विद्दुत चालित अभिकलित्र से है। तब से अबतक यह आकार में क्रमशः
छोटा और संक्रिया की दृष्टि से अत्यधिक समर्थ होता गया हैं। अब अभिकलक घड़ी
के अन्दर समा सकते हैं और विद्युत कोष (बैटरी) से चलाये जा सकते हैं। निजी अभिकलक के विभिन्न रूप जैसे कि सुवाह्य संगणक, टैबलेट आदि रोजमर्रा की जरूरत बन गए हैं।
अभिकलित्र के भाग
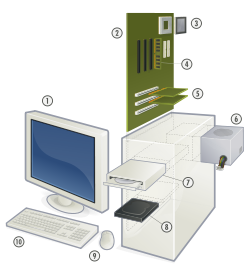
निजी अभिकलित्र (पीसी) के प्रमुख भाग एक अभिकलित्र (संगणक) निम्नलिखित चार भागों से मिलकर बनता है : निविष्ट यंत्र , संसाधन यंत्र , निर्गम यंत्र और भंडारण यंत्र।
(युक्ति को यंत्र भी कहा जता है।)
निविष्ट यंत्र(इनपुट डिवाइस)
- निविष्ट यंत्र या इनपुट डिवाइस उन उपकरणों को कहते हैं जिसके द्वारा निर्देशो और आंकडों को संगणक में भेजा जाता है। जैसे- कुन्जी पटल (की-बोर्ड), माउस, जॉयस्टिक, ट्रैक बाल आदि।
केंद्रीय प्रक्रमन इकाई
- केंद्रीय प्रक्रमन इकाई (सीपीयू),
संसाधन युक्ति या विचार युक्ति - यह अभिकलित्र की मूल संक्रियात्मक इकाई
है जो आगम उपकरणों द्वारा दिए गए आंकड़ों के अनुरूप कार्य कर उसे निर्गत
इकाई को भेजती है। इसके तीन भाग होते हैं:
- बही या पंजी (रजिस्टर) - सबसे पहले जिन आंकड़ों या सूचनाओं पर काम करना होता है, उन्हें अभिकलित्र स्मृति से बही में अंकित किया जाता है। अलग अलग प्रक्रियाओं के लिए अलग अलग बही होते हैं आंकिक एवं तर्क इकाई की संक्रिया के बाद सूचनाएं पुनः बही में दर्ज होती हैं और वापस स्मृती में भेजी जाती हैं।
- आंकिक एवं तर्क इकाई - यह इकाई बही में दर्ज सूचनाओं पर निर्देशों के अनुसार कार्य करती है तथा परिणाम को पुनः उपयुक्त बही में दर्ज कर देता है।
- नियन्त्रण इकाई - यह केंद्रिय प्रसाधन इकाई की सभी क्रियाओं का नियंत्रण करती है। जैसे कि स्मृति से सूचनाएं बही में वहाँ से आंकिक एवं तर्क इकाई में, वापस बही में तथा वहाँ से स्मृति में वापस जाने की प्रक्रिया पर यह इकाई नियंत्रण रखती है।
सूचना भंडारण उपकरण
पीसी में प्रयुक्त 64MB एसडीरैम (SDRAM)
- सूचना भंडारण उपकरण या सुरक्षण उपकरण - यह अभिकलित्र में प्रयुक्त सूचनाएं सहेजती है।
- अल्पकालिक भंडारण उपकरण - कम समय तक सूचना के भंडारण के लिये
- यादृच्छिक अभिगम स्मृति या रैम (RAM)|रैंडम एक्सैस मैमोरी (रैम)
- पठन स्मृति या रीड ओन्ली मेमोरी (रौम)
- दीर्घकालिक भंडारण उपकरण - लंबे समय तक सूचना के भंडारण के लिये
- हार्ड ड्राइव या हार्ड डिस्क
- हटाये जा सकने वाला भंडारण उपकरण
- नम्यिका (फ्लॉपी डिस्क)
- कॉम्पैक्ट डिस्क (सीडी)
- अंकीय वीडियो डिस्क (डीविडी)
- चपला स्मृति भंडारण युक्ति या फ्लैश मेमोरी स्तोरेज डिवाइस
- यूऍसबी फ्लैश ड्राइव या फ्लैश मेमोरी ड्राइव
- फ्लैश मेमोरी कार्ड या फ्लैश मेमोरी स्तिक
- ब्ल्यू-रे डिस्क
- अल्पकालिक भंडारण उपकरण - कम समय तक सूचना के भंडारण के लिये
निर्गम यंत्र
- निर्गम यंत्र
(आउटपुट डिवाइस)- इसमें वे सभी उपकरण शामिल हैं जिनसे प्रसाधित सूचनाएं या
सामग्री मानवीय उपयोगी उत्पाद के रूप में बाहर आती हैं॥ जैसे-
- प्रदर्शक (मॉनिटर) - इसकी सहायता से प्रसाधित सामग्री दृश्य रूप में प्रकट होती है॥
- स्क्रीन स्क्रीन पर चित्र य चल्चित्र प्रकत होते है। ये प्रदर्शक से जुडा होता है।
- मुद्रक- इसकी सहायता से निर्गत सामग्री को कागज़ पर मुद्रित किया जाता है। इसे अन्ग्रेजी भाषा में प्रिनटर भी कहते है।
- भोंपू - इसे स्पीकर भी कह्ते है, जैसा कि नाम से ही पता चलता है, ये आवाज निकालने का काम करता है। इसका उपयोग अभिकलित्र में चालू किसी भि प्रक्रिया से उत्पन्न आवाज को उपयोगकर्ता तक पहुचाने के लिये किया जाता है।
- प्रदर्शक (मॉनिटर) - इसकी सहायता से प्रसाधित सामग्री दृश्य रूप में प्रकट होती है॥
अभिकलित्र के प्रकार
अभिकलित्र
का मुख्य कार्य दिये गये आंकड़े को जमा कर उसपर दिए गए निर्देशों के
अनुरूप काम कर परिणाम देना है॥ कार्यक्षमता के आधार पर इसे निम्नलिकित
श्रेणियों में बाँटा गया है- सुपर संगणक, मेनफ्रेम संगणक मिनी संगणक, एव
माइक्रो संगणक आदि। सुपर संगणक इनमें सबसे बडी श्रेणी होती है, तथा माइक्रो
संगणक सबसे छोटी।
- सुपर संगणक सबसे तेज गति से कार्य करने वाले संगणक होते हैं। वह बहुत अधिक डाटा को काफी कम समय में इंफार्मेशन में बदलने में सक्षम होते हैं। इनका प्रयोग बड़े-बड़े कार्य करने में होता है, जैसे मौसम की भविष्यवाणी, डाटा माइनिंग, जटिल सिमुलेशन, मिसाइलों के डिजाइन आदि। इनमें अनेक माइक्रोप्रोसेसर [एक विशेष छोटी मशीन जो कम्प्यूटिंग के कार्य को काफी आसानी से तथा बहुत ही कम समय में कर सकने में सक्षम होती है।] लगे होते हैं। किसी जटिल गणना को कम समय में पूरा करने के लिये बहुत से प्रोसेसर एकसाथ (पैरेलेल) काम कराने पडते हैं। इसे पैरेलेल प्रोसेसिंग कहा जाता है। इसके अन्तर्गत जटिल काम को छोटे-छोटे टुकडों में इस प्रकार बाँटा जाता है कि ये छोटे-छोटे कार्य एक साथ अलग-अलग प्रोसेसरों द्वारा स्वतन्त्र रूप से किये जा सकें।
- मेनफ्रेम संगणक, सुपर संगणक से कार्यक्षमता में छोटे परंतु फिर भी बहुत शक्तिशाली होते हैं। इन कम्प्यूटरों पर एक समय में २५६ से अधिक व्यक्ति एक साथ काम कर सकते हैं। अमरीका की आईबीएम कंपनी मेनफ्रेम कंप्युटरों को बनाने वाली सबसे बडी कंपनी है।
- मिनी संगणक मेनप्रेम कंप्यूटरों से छोटे परnतु माइक्रो कम्प्यूटरों से बड़े होते हैं।
- माइक्रो संगणक (पर्सनल संगणक) सबसे छोटे होते हैं तथा इन्हीं को वैयक्तिक संगणक या पर्सनल संगणक भी कहा जाता है। इसका प्रथम संस्करण १९८१ में विकिसित हुआ था, जिसमे ८०८८ माइक्रोप्रोसेसर प्रयुक्त हुआ था।
- मेज के ऊपर रखने लायक संगणक (डेस्कटॉप)
- गोद के ऊपर रखने लायक संगणक (लैपटॉप)
- हथेली के ऊपर रखने लायक संगणक (पाल्म्टॉप) - स्मार्टफोन, संगीत खिलाड़ी (म्यूजिक प्लयेर), वीडियो खिलाड़ी (वीडियो प्लेयर)
- टैबलेट संगणक
अभिकलित्र के गुण
संगणक हमारे द्वारा दिये जाने वाले हर कार्य को बखूबी करने में सक्षम होते हैं। इनके कुछ गुण इस प्रकार हैं :
- गति
- संगणक काफी तेज गति से कार्य करते हैं, जब हम संगणक के बारे में बात करते हैं, तो हम मिनी सेकेन्ड, माइक्रो सेकेन्ड में बात नहीं करते, बल्कि हम 10-12 सेकेन्ड में एक कम्पयूटर कितना कार्य कर लेता है, इस रूप में उसकी गति को आँकते हैं।
- न उबना
- संगणक कभी भी उबते (बोर) नहीं हैं और यही इनका सबसे अच्छा गुण है, क्योंकि यह एक यंत्र हैं, इसलिये ये काफी दिनों तक बिना किसी शिकायत के कार्य करने में सक्षम होते हैं।
- स्मरण करने या संग्रह की क्षमता
एक सामान्य संगणक भी एक बार दिये गये निर्देश को काफी समय तक स्मरण रखने
में सक्षम होता है, तथा जब भी आवश्यकता पडे़, उसे फिर से लिखा और भरा जा
सकता है।
इतिहास
बीसवीं शताब्दी से पहले के संगणक उपकरण
यांत्रिक रेखीय (एनालॉग)
संगणकों का प्रादुर्भाव प्रथम शताब्दी में होना शुरू हो गया था जिन्हे बाद
में मध्यकालीन युग में खगोल शास्त्रीय गणनाओ के लिए इस्तेमाल भी किया गया।
यांत्रिक रेखीय संगणकों को द्धितीय विश्व युद्ध के दौरान विशेषीकृत सैन्य कार्यो में उपयोग किया गया। इसी समय के दौरान पहले विद्दुतीय अंकीय परिपथ वाले संगणको का विकास हुआ। प्रारम्भ में वो एक बड़े कमरे के आकार के होते थे और आज के आधुनिक सैकड़ों निजी संगणकों [3] के बराबर बिजली का उपभोग करते थे।
पहली इलेक्ट्रॉनिक अंकीय संगणक यूनाइटेड किंगडम और संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका में 1940 और 1945 के बीच विकसित किया गया।
गणनाएँ करने के लिये यन्त्रो का इस्तेमाल हज़ारो वर्षो से होता आ
रहा है खासकर उग्लियो से गिनती करने वाले उपकरणो का। शुरुवाती गणन यन्त्र
सम्भवत: मिलान छड़ी|वो लकड़ी जिस पर गिनती के लिये दांत खोदे गये हो या मिलान छड़ी का एक रूप थी। बाद में मध्य पूर्व में उपजाऊ भूमि के एक भौगोलिक क्षेत्र जो कि आकार में अर्द्ध चंद्र जैसा दिखता है में अभिलिेखो को रखने के लिए कॅल्क्युली
(मिटटी के गोले, शंकु) का इस्तेमाल होता रहा जो की अधपके और खोखले मिटटी
के बर्तनो में रखा होता था। इनका उपयोग सामान की गिनती (अधिकतर पशुधन व
अनाज) दर्शाने के लिए किया जाता था। [4][5] गिनती की छड़े|गिनती की छड़ों का उपयोग इसका एक उदहारण है।
स्वन पन (इस गिनतारे पर प्रदर्शित हो रही संख्या है ६,३०२,७१५,४०८)
शुरुवात में गिनतारे का उपयोग अंकगणितीय कार्यो के लिए होता था। जिसे आज हम रोमन गिनतारा कहते है उसका उपयोग २४०० ईसा पूर्व के प्रारम्भ में बेबीलोनिआ
में हुआ था। तब से अब तक गड़ना व हिसाब लगाने के लिए कई अन्य गणन् पट्टियो
व गोलियो का आविश्कार हो चुका है। एक मध्ययुगीन युरोपीय गडना घर|गड़ना घर
में मेज पर चितकबरे कपडे को रख दिया जाता था और कुछ विशेष नियमो के अनुसार
उसपर मोहरों को चलाकर पैसे जोड़ने के लिए एक साधन के तौर पे इस्तेमाल किया
जाता था।
प्राचीन यूनानी रूपरेखा वाले एंटीकाईथेरा प्रक्रिया १५० से १०० ईसा पूर्व के समय के दुनिया के सबसे पुराने रेखीय संगणक हैं।
प्राचीन और मध्ययुगीन कालों में खगोलीय गणनाओं के निष्पादन के लिए कई एनालॉग कंप्यूटरों
का निर्माण किया गया था। इनमें शामिल हैं प्राचीन ग्रीस की एंटिकिथेरा
प्रक्रिया और एस्ट्रॉलैब (लगभग 150-100 ईसा पूर्व), जिन्हें आम तौर पर सबसे
प्रारंभिक ज्ञात यांत्रिक एनालॉग कंप्यूटर माना जाता है।[8]
एक या अन्य प्रकार की गणनाओं के निष्पादन के लिए इस्तेमाल किये जाने वाले
यांत्रिक उपकरणों के अन्य प्रारंभिक संस्करणों में शामिल हैं प्लेनिस्फेयर
और अबू रेहान अल बिरूनी (Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī) (लगभग 1000 ईसा पश्चात्)
द्धारा आविष्कृत अन्य यांत्रिक संगणन उपकरण; अबू इसहाक इब्राहिम अल
ज़र्काली (Abū Ishāq Ibrāhīm al-Zarqālī) (लगभग 1015 ईसा पश्चात्) द्वारा
आविष्कृत इक्वेटोरियम और यूनिवर्सल लैटिट्यूड-इंडिपेंडेंट एस्ट्रोलेबल;
अन्य मध्ययुगीन मुस्लिम खगोलविदों और इंजीनियरों के खगोलीय एनालॉग
कंप्यूटर; और सोंग राजवंश के दौरान सू सोंग (लगभग 1090 ईसा पश्चात्) का
खगोलीय क्लॉक टावर।
अल जजारी द्वारा 1206 में आविष्कृत एक खगोलीय घड़ी को सबसे पहला प्रोग्राम योग्य रेखीय संगणक माना जाता है।[9]
यह राशि चक्र, सूर्य और चंद्रमा की कक्षाओं को दर्शाती थी, इसमें एक
अर्द्ध-चंद्राकार सूचक एक संपूर्ण प्रवेश द्वारा से होकर गुजरती थी जिसके
कारण हर घंटे पर स्वचालित द्धार खुल जाते थे[10][11] और पांच रोबोटिक संगीतकार जो एक पानी के पहिये (वाटर व्हील) से जुड़े कैमशाफ्ट द्वारा संचालित लीवरों
द्वारा मारे जाने पर संगीत बजा दिया करते थे। दिन और रात की लंबाई को वर्ष
भर में दिन और रात की बदलती लंबाइयों के लिए उपयुक्त बनाने के क्रम में हर
दिन फिर से प्रोग्राम किया जा सकता है।[9]
संगणक के विकास का संक्षिप्त इतिहास
- 1623 ई.: जर्मन गणितज्ञ विल्हेम शीकार्ड ने प्रथम यांत्रिक कैलकुलेटर का विकास किया। यह कैलकुलेटर जोड़ने, घटाने, गुणा व भाग में सक्षम था।
- 1642 ई.: फ्रांसीसी गणितज्ञ ब्लेज़ पास्कल ने जोड़ने व घटाने वाली मशीन का आविष्कार किया।
- 1801 ई.: फ्रांसीसी वैज्ञानिक जोसेफ मेरी जैकार्ड ने लूम (करघे) के लिए नई नियंत्रण प्रणाली का प्रदर्शन किया। उन्होंने लूम की प्रोग्रामिंग की, जिससे पेपर कार्डों में छेदों के पैटर्न के द्वारा मशीन को मनमुताबिक वीविंग ऑपरेशन (weaving operation) का आदेश दिया जाना सम्भव हो गया।
- 1833-71 ई.: ब्रिटिश गणितज्ञ और वैज्ञानिक चार्ल्स बैबेज ने जैकार्ड पंच-कार्ड प्रणाली का प्रयोग करते हुए 'एनालिटिकल इंजन' का निर्माण किया। इसे वर्तमान कम्प्यूटरों का अग्रदूत माना जा सकता है। बैबेज की सोच अपने काल के काफी आगे की थी और उनके आविष्कार को अधिक महत्व नहीं दिया गया।
- 1889 ई.: अमेरिकी इंजीनियर हरमन हॉलेरिथ ने 'इलेक्ट्रो मैकेनिकल पंच कार्ड टेबुलेटिंग सिस्टम' को पेटेंट कराया जिससे सांख्यिकी आँकड़े की भारी मात्रा पर कार्य करना सम्भव हो सका। इस मशीन का प्रयोग अमेरिकी जनगणना में किया गया।
- 1941 ई.: जर्मन इंजीनियर कोनार्डसे ने प्रथम पूर्णतया क्रियात्मक डिजिटल कम्प्यूटर Z3 का आविष्कार किया जिसे प्रोग्राम द्वारा नियंत्रित किया जा सकता था। Z3 इलेक्ट्रॉनिक कम्प्यूटर नहीं था। यह विद्युतीय स्विचों पर आधारित था जिन्हें रिले कहा जाता था।
- 1942 ई.: आइओवा स्टेट कॉलेज के भौतिकविद जॉन विंसेंट अटानासॉफ और उनके सहयोगी क्लिफोर्ड बेरी ने प्रथम पूर्णतया इलेक्ट्रॉनिक कम्प्यूटर के कार्यात्मक मॉडल का निर्माण किया जिसमें वैक्यूम ट्यूबों का प्रयोग किया गया था। इसमें रिले की अपेक्षा तेजी से काम किया जा सकता था। यह प्रारंभिक कम्प्यूटर प्रोग्रामेबल नहीं था।
- 1944 ई.: आईबीएम और हार्वर्ड यूनीवॢसटी के प्रोफेसर हॉवर्ड आइकेन ने प्रथम लार्ज स्केल ऑटोमेटिक डिजीटल कम्प्यूटर 'मार्क-1' का निर्माण किया। यह रिले आधारित मशीन 55 फीट लम्बी व 8 फीट ऊँची थी।
- 1943 ई.: ब्रिटिश वैज्ञानिकों ने द्वितीय विश्वयुद्ध के दौरान जर्मन कोडों को तोडऩे के लिए इलेक्ट्रॉनिक कम्प्यूटर 'कोलोसस' का निर्माण किया।
- 1946 ई.: अमेरिकी सेना के लिए पेनसिल्वेनिया विश्वविद्यालय में भौतिकविद् जॉन माउचली और इंजीनियर जे. प्रेस्पर इकेर्ट ने 'इलेक्ट्रॉनिक न्यूमेरिकल इंटीग्रेटेड एंड कम्प्यूटर - इनिएक' (ENIAC) का निर्माण किया। इस कमरे के आकार वाले 30 टन कम्प्यूटर में लगभग 18,000 वैक्यूम ट्यूब लगे थे। इनिएक की प्रोग्रामिंग अलग-अलग कार्य करने के लिए की जा सकती थी।
- 1951 ई.: इकेर्ट और माउचली ने प्रथम कॉमर्शियल कम्प्यूटर 'यूनिवेक' (UNIVAC) का निर्माण किया (सं.रा. अमेरिका)।
- 1969-71 ई.: बेल लेबोरेटरी में 'यूनिक्स ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम' का विकास किया गया।
- 1971 ई.: इंटेल ने प्रथम कॉमॢशयल माइक्रोप्रोसेसर '4004' का विकास किया। माइक्रोप्रोसेसर चिप पर सम्पूर्ण कम्प्यूटर प्रोग्रामिंग यूनिट होती है।
- 1975 ई.: व्यावसायिक रूप से प्रथम सफल पर्सनल कम्प्यूटर 'MITS Altair 8800' को बाजार में उतारा गया। यह किट फार्म में था जिसमें की-बोर्ड व वीडियो डिस्प्ले नहीं थे।
- 1976 ई.: पर्सनल कम्प्यूटरों के लिए प्रथम वर्ड प्रोग्रामिंग प्रोग्राम 'इलेक्ट्रिक पेंसिल' का निर्माण।
- 1977 ई.: एप्पल ने 'एप्पल-II' को बाजार में उतारा, जिससे रंगीन टेक्स्ट और ग्राफिक्स का प्रदर्शन संभव हो गया।
- 1981 ई.: आई बी एम ने अपना पर्सनल कम्प्यूटर बाजार में उतारा जिसमें माइक्रोसॉप्ट के DOS (डिस्क ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम) का प्रयोग किया गया था।
- 1984 ई.: एप्पल ने प्रथम मैकिंटोश बाजार में उतारा। यह प्रथम कम्प्यूटर था जिसमें GUI (ग्राफिकल यूज़र इंटरफेस) और माउस की सुविधा उपलब्ध थी।
- 1990 ई.: माइक्रोसॉफ्ट ने अपने ग्राफिकल यूज़र इंटरफेस का प्रथम वजऱ्न 'विंडोज़ 3.0' बाजार में उतारा।
- 1991 ई.: हेलसिंकी यूनीवर्सिटी के विद्यार्थी लाइनस टोरवाल्ड्स ने पर्सनल कम्प्यूटर के लिए 'लाइनेक्स' का आविष्कार किया।
- 1996 ई.: हाथ में पकड़ने योग्य कम्प्यूटर 'पाम पाइलट' को बाजार में उतारा गया।
- 2001 ई.: एप्पल ने मैकिंटोश के लिए यूनिक्स आधारित ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम 'Mac OS X' को बाजार में उतारा।
- 2002 ई.: कम्प्यूटर इंडस्ट्री रिसर्च फर्म गार्टनेर डेटा क्वेस्ट के अनुसार 1975 से वर्तमान तक मैन्यूफैक्चर्ड कम्प्यूटरों की संख्या 1 अरब पहुँची।
- 2005 ई.: एप्पल ने घोषणा की कि वह 2006 से अपने मैकिंटोश कम्प्यूटरों में इंटेल माइक्रोप्रोसेसरों का प्रयोग आरंभ कर देगा।
- विभिन्न प्रकार के कम्प्यूटर
- नासा का कोलम्बिया सुपकम्प्यूटर (2004)